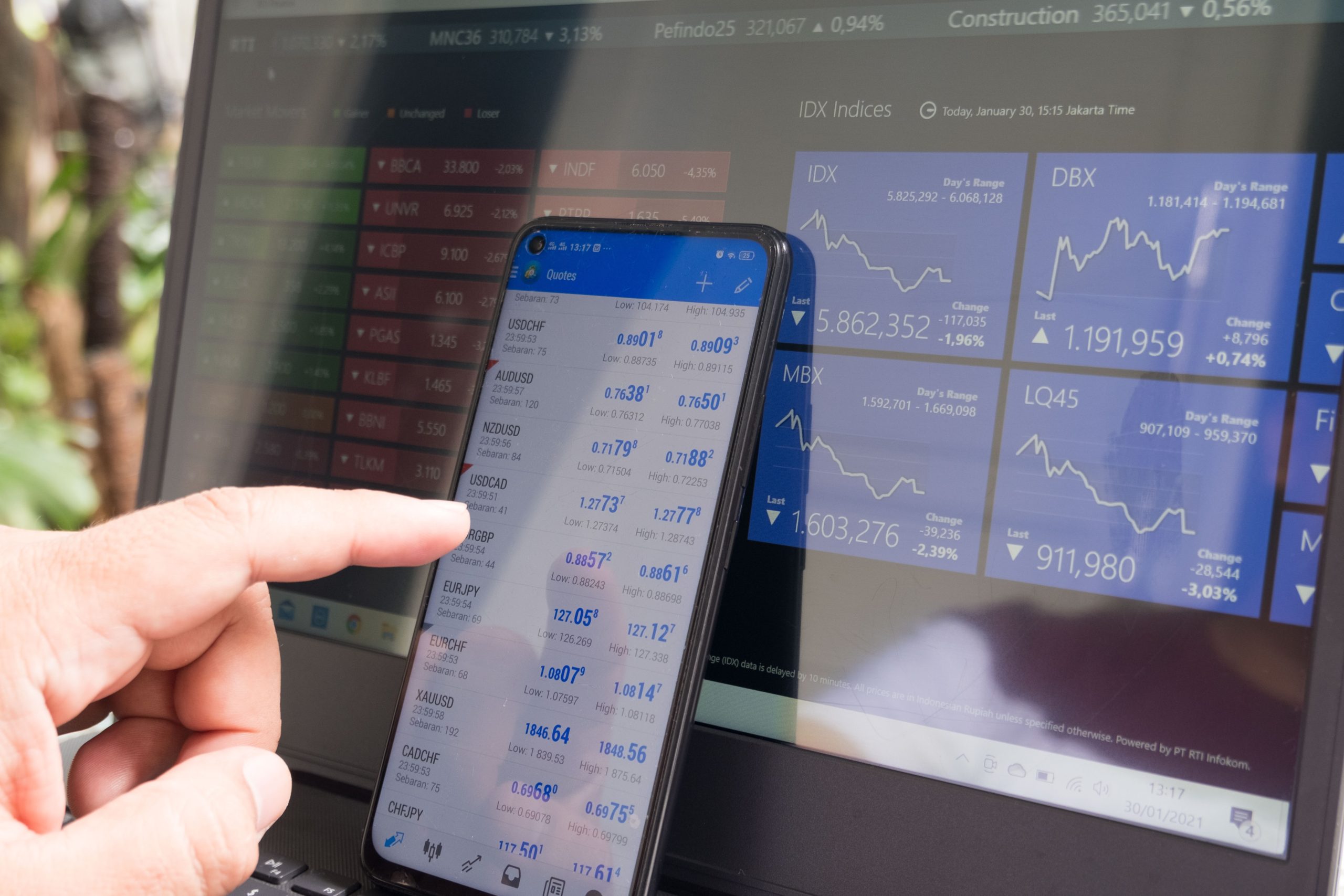
[ I have briefly illustrated all simple and basic terms in this article. However, I didn’t go through each of them in-depth. In case you want to know more, I have built an external link for each word, and you could go to take a look for a more detailed explanation]
Foreword
When talking about stock trading or investing, there are several must-know terms you are to know. I’ll provide brief definitions of all of them and give you easy-to-be-understood examples so that you can become familiar with them. Learn them all.
Basic Terms of Stock Trading/Investing
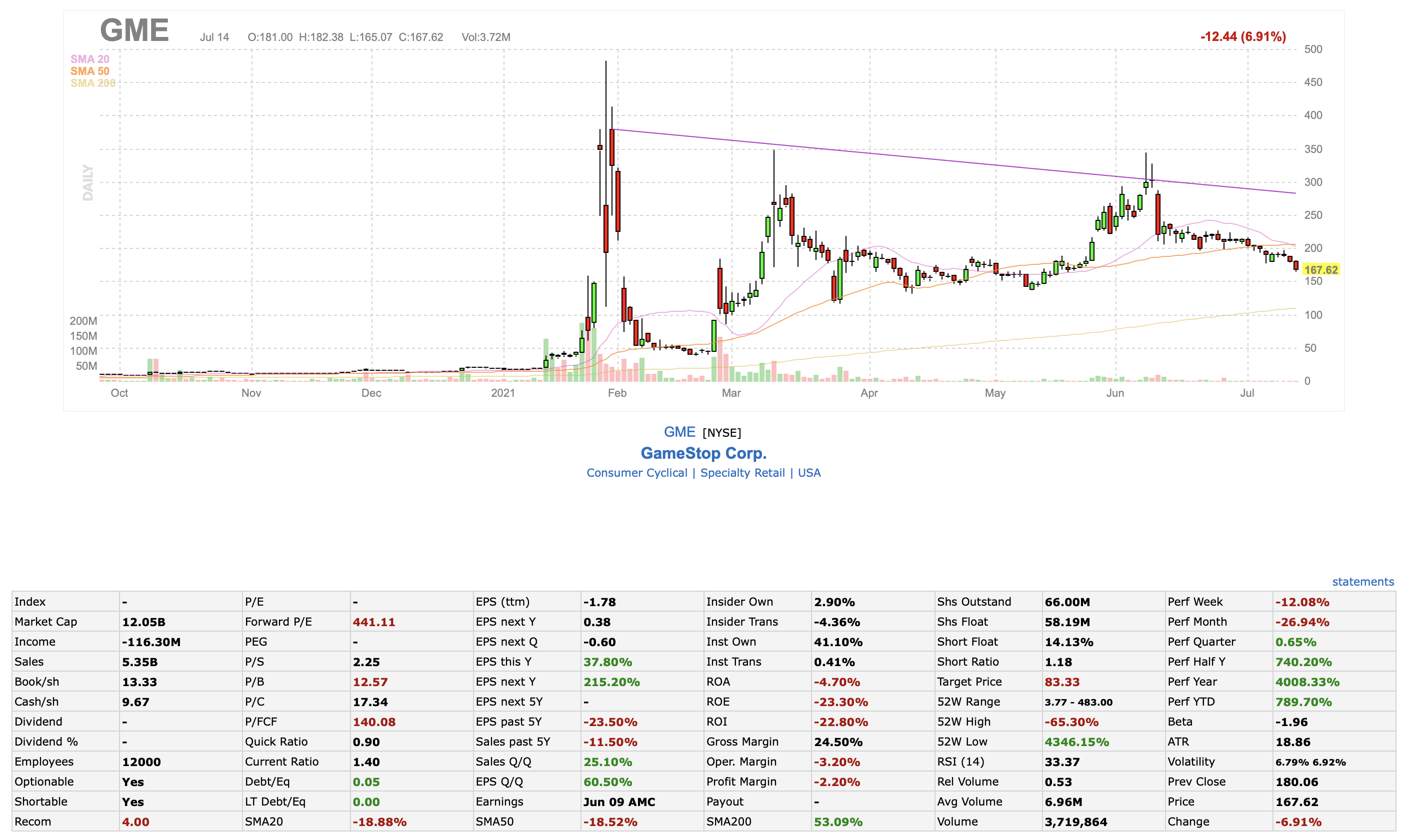
You may see there are numerous things on the table that may frighten you. Don’t worry. You are not supposed to learn them all today. In this article, we are just going through some basic terms that you must-know to start learning stocks.
(other terms would be covered in later post)
1. Ticker
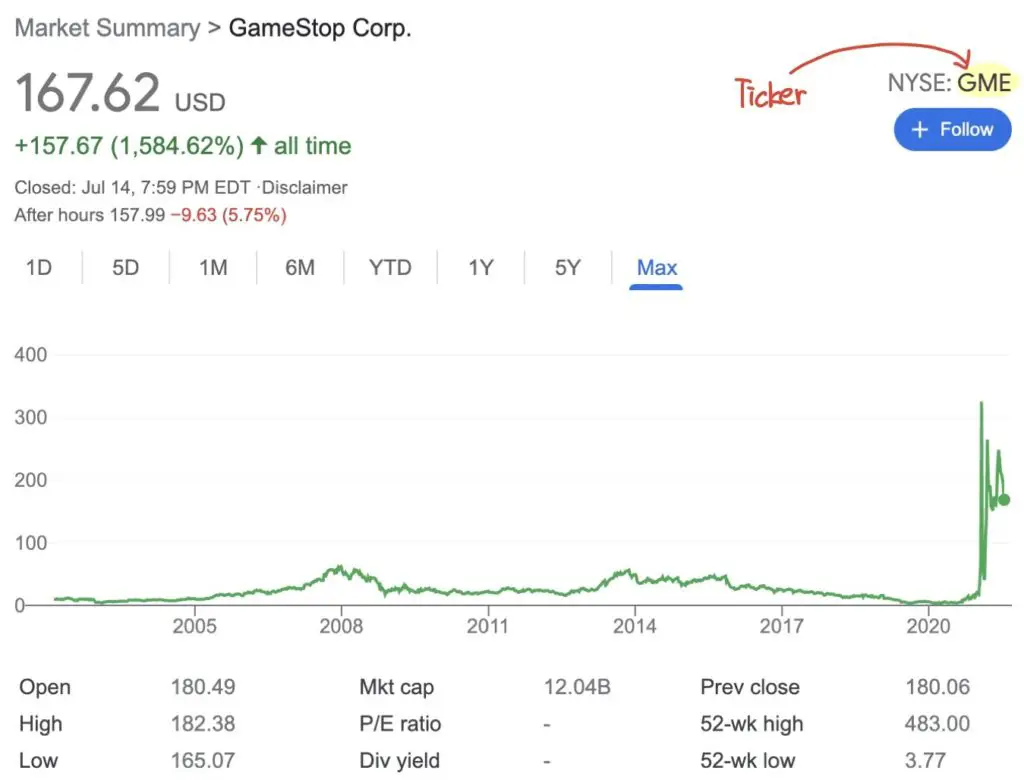
Ticker is the short form of a company’s name. Often we use ticker to search stock information of a company. For example, GME is the ticker of GameStop Corp. CIA.
(You can search any company’s ticker you want by typing the (company name) (stock) on Google)
2. Public Listed Company
A public listed company is a company that issues its shares to the public for raising money.
3. Private Company
A private company is a company which only allows private investor invest in their company. Without connection, we are not able to invest in these companies.
4. Initial Public Offering (IPO)
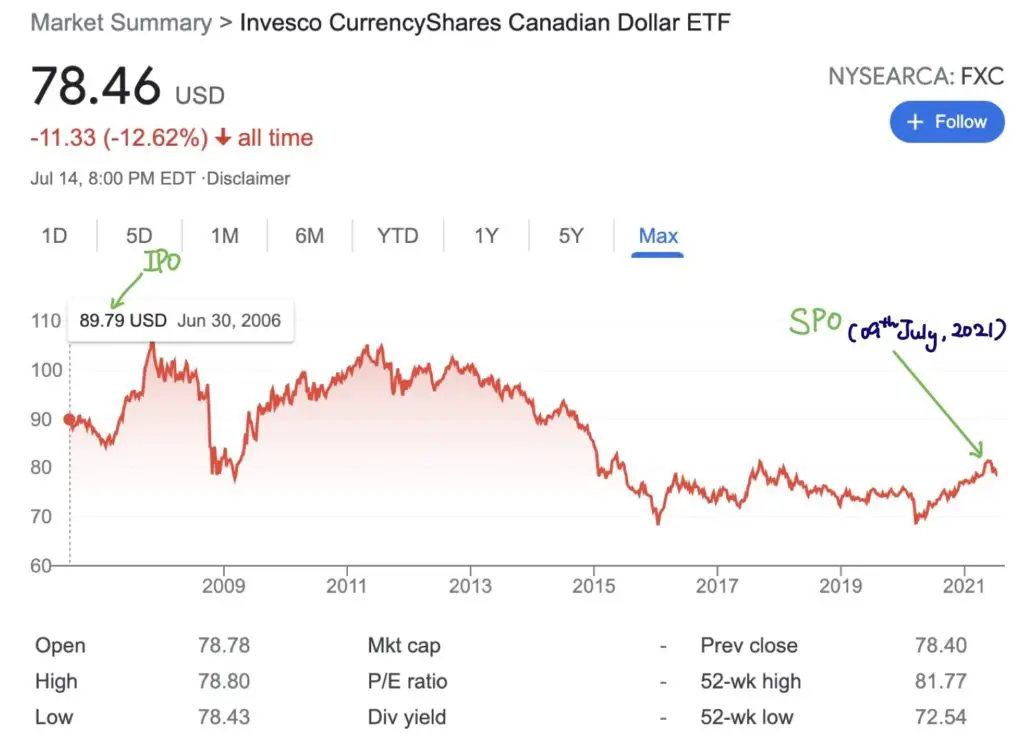
Initial Public Offering (IPO) is the first time that company issues its shares to the public. In other words, it’s the first time people could buy stocks of the company.
Recent IPO: NYSE IPO Filings
5. Secondary Public Offering (SPO)
Secondary Public Offering is the shares issuing by a company after the IPO. It doesn’t matter if they are making the offer for the second time or the third time. They all are called secondary offerings. Often, the secondary offering would dilute the share price of the stock.
6. Stock/Share
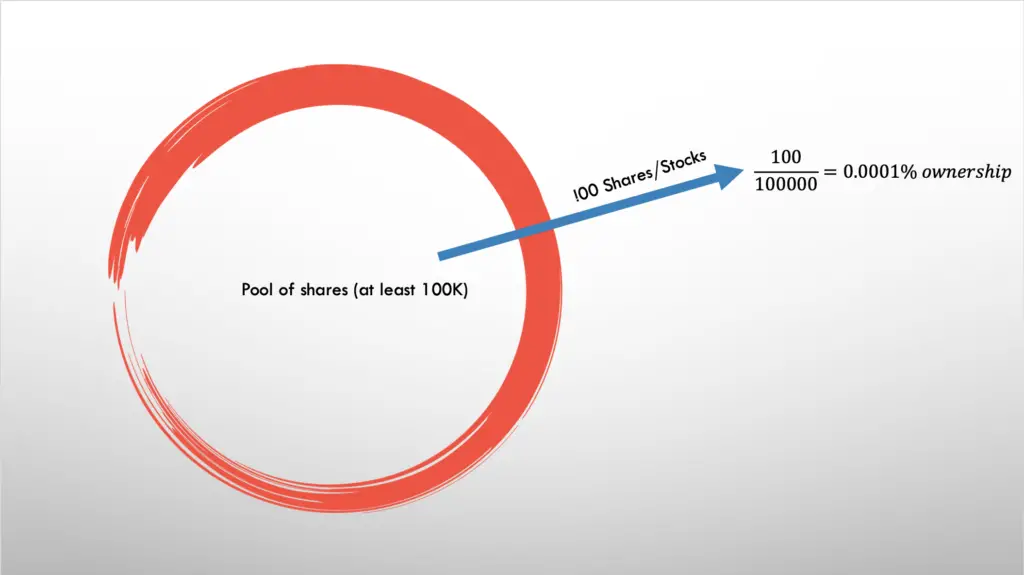
A stock/ share is the basic unit we use to determine the degrees of ownership we got in a company. Often, companies would issue at least 100K shares to raise money.
7. Institutional Ownership
Institutional ownership is the number of shares/stocks owned by the insider, mutual funds, insurance company, investment firms or private investor of that company. When calculating your degree of ownership in a company, you need to include that in the equation.
8. Float
Float is the total amount of shares that could be bought or sold by the general public in the stock market.
9. Share Outstanding
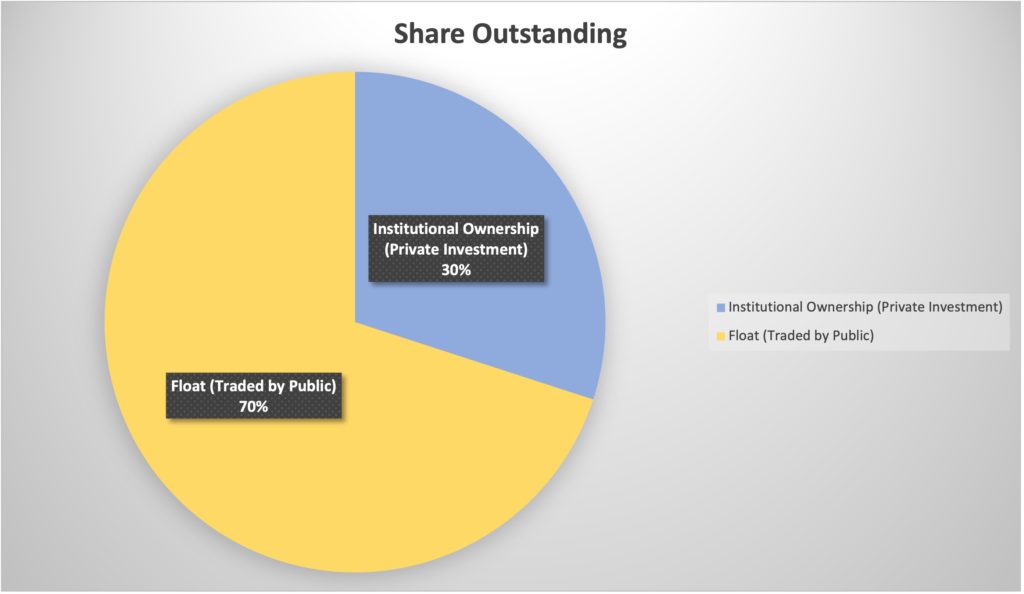
Share Outstanding is the total amount of shares that a company has issued. To calculate the share outstanding of a company, you need to sum up the float and the Share owned by private investors or insiders of the company (Institutional ownership)
10. Stock Quote
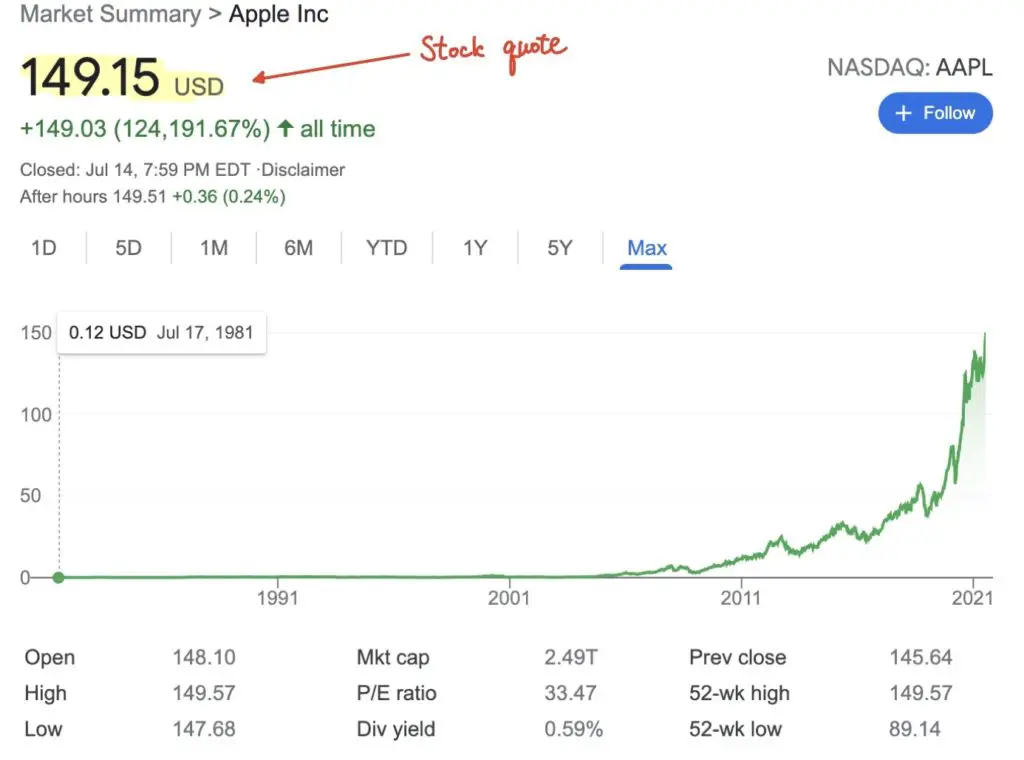
Stock Quote is the market price of a share.
11. Market Capitalisation (Market Cap)
Market Capitalization (Market Cap) is the total price of shares issued by a company. To calculate the Market Cap of a company, you need to multiply the share outstanding of the company and the stock quote.
12. Exchanges
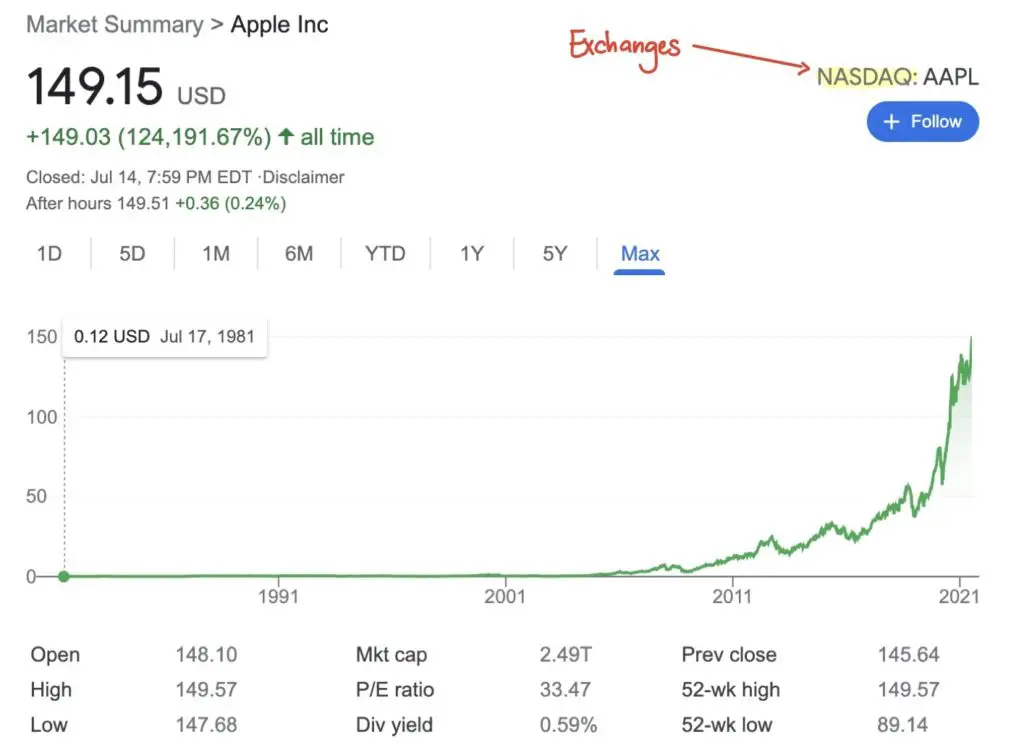
An exchange is a place where securities are traded. Often they use Electronic communication network (ECN) to deal with our orders. There are numerous exchanges in U.S. You can go and take a look at them by clicking here.
13. Position
Having a position means you did long or short sell security. Often, people say they hold a ____ (Long/Short) position.
14. Long
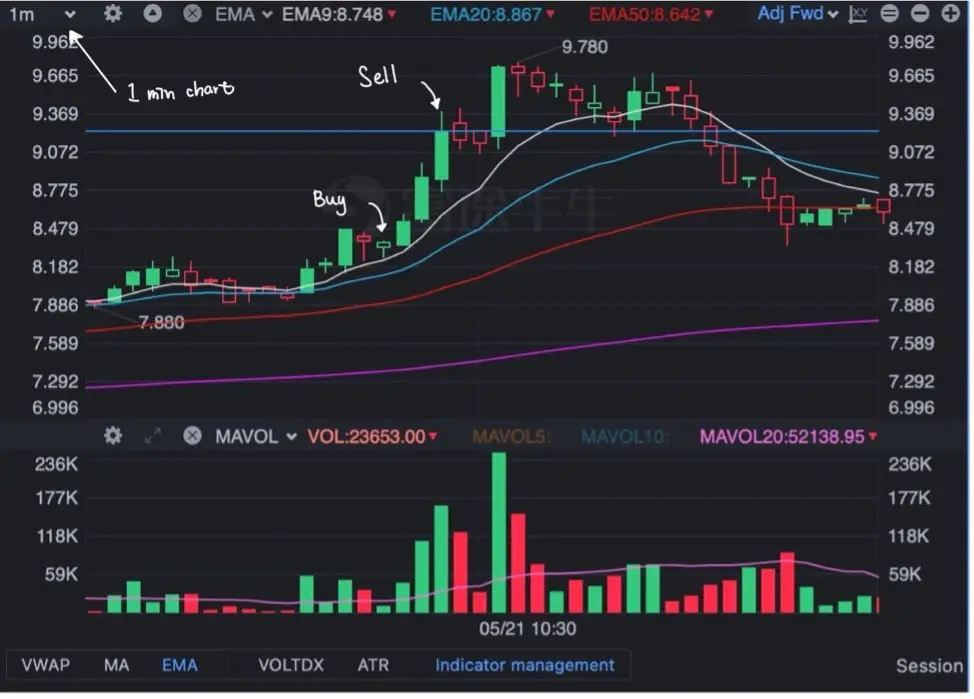
Having a “Long” position in security means that you own the security. Traders/Investors could make a profit when they buy the security at a low price and then sell them at a high price.
15. Short and Cover
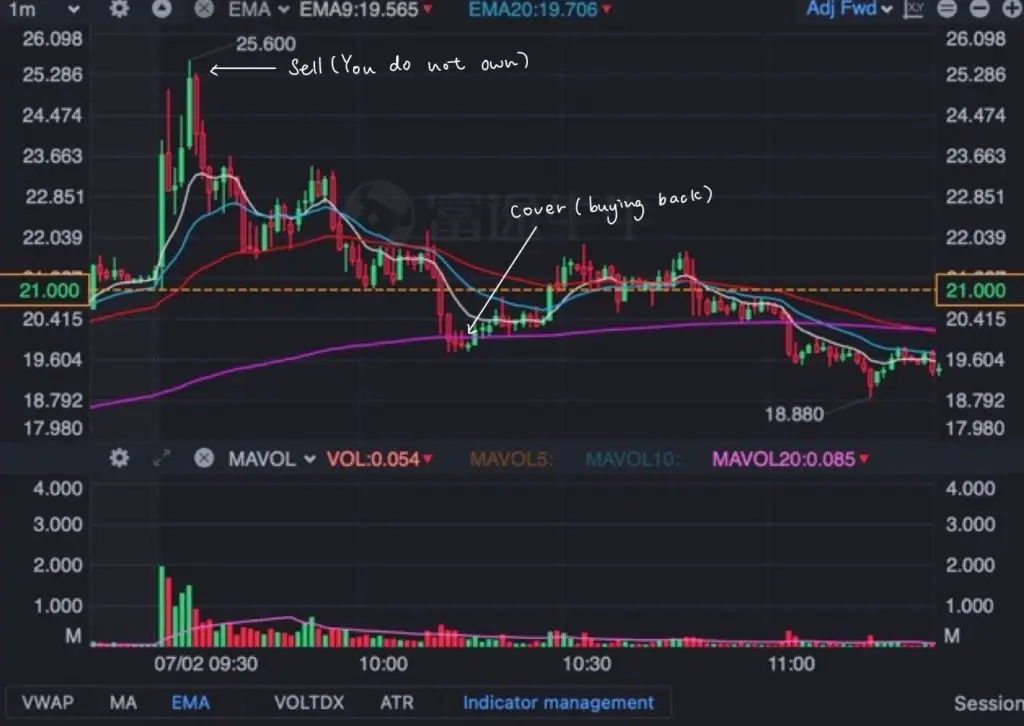
Having a “Short” position in security means that you sell a security that you do not own (borrowed from your broker). Traders/Investors could earn a profit when they first sell the security (not own) and then cover their position when the security price is low.
“Cover” is a term that depicts the action of Traders/Investors buying back the security that they do not own when they are selling short.
16.Bear Market / Bearish
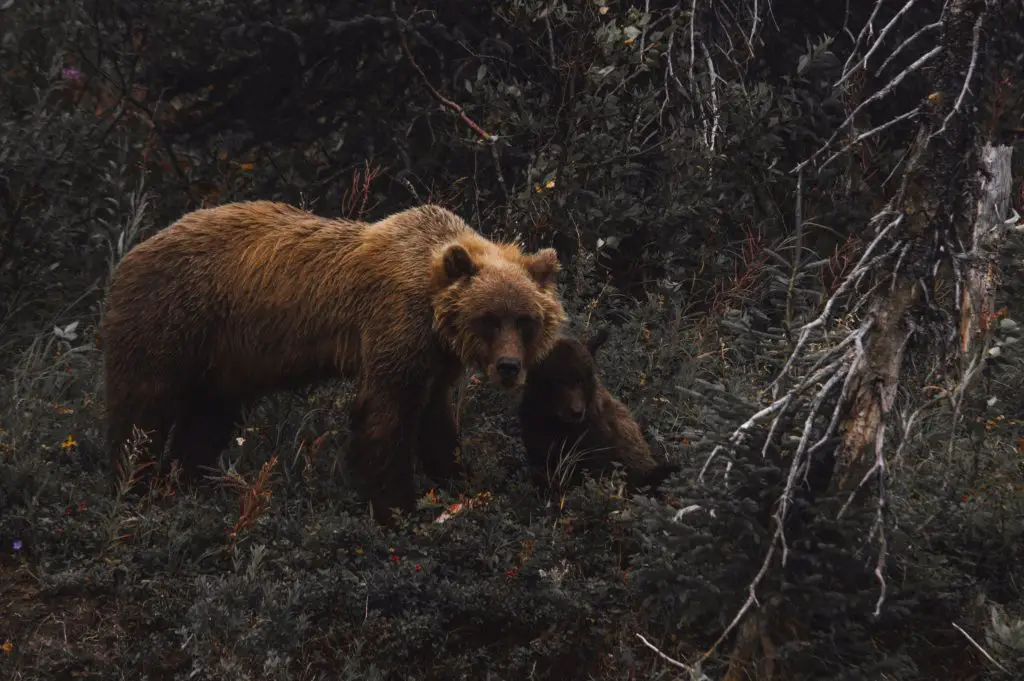

Do you know how bears attack? Bears attack by rearing up on their hind legs, knock victims over with their paws, and push them down. People say the market is bearish when they see the trend of a market is going downward. The reason people are using a bear to describe a market is since the way bear attacks look like a downward trend.
17. Bull Market / Bullish
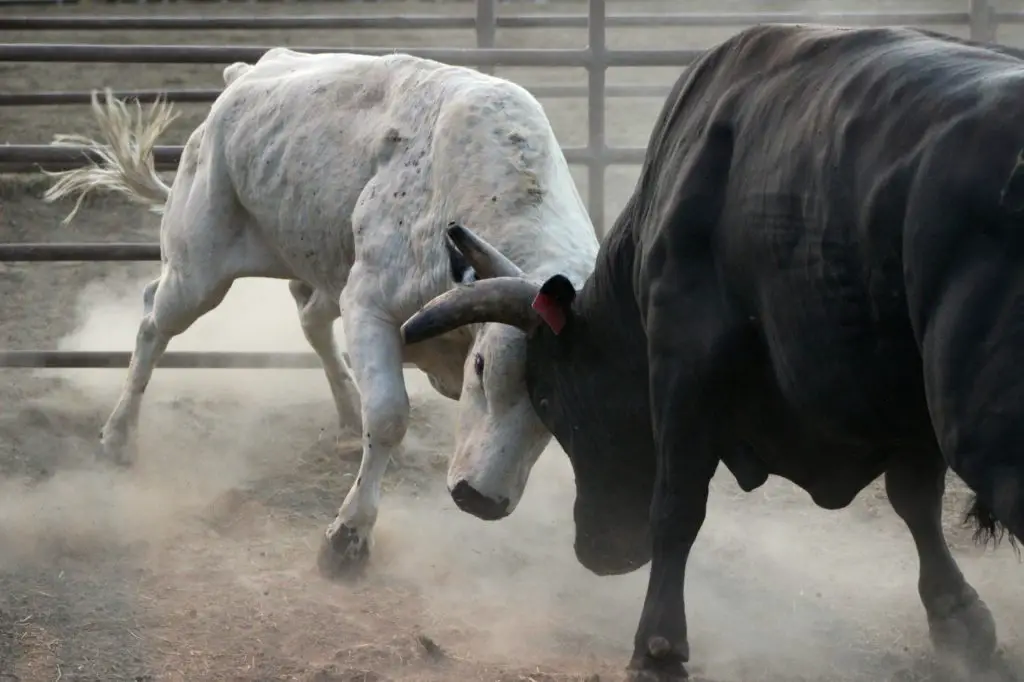

Do you know how bulls attack? Bulls attack by rushing into victims and push them upward. People say the market is bullish when they see the trend of a market is going upward (Uptrend). The reason people are using a bull to describe a market is since the way bull attacks look like an uptrend trend.
Final Thought
Make sure you get familiar with them before you put real money into the market. I may update this post if I find some words that may be helpful for you to build your foundation. You could get back to this post if you forget one of them.
[Next Lesson: Long buying vs Short selling]